Natural Omega 3 fish oil in fish gelatine
- 500mg of pure fish oil with natural lemon flavour
- Screened for toxins & heavy metals
- Bio-Fish Oil is manufactured to pharmaceutical standards
- The oil comes from the flesh of the fish, not the liver
- For normal heart function, normal vision & normal brain function
- Capsules can be swallowed, cut open or chewed
- Gluten Free / Lactose Free / Soy Free / Yeast Free / Sugar Free
Bio-Fish Oil
Bio-Fish Oil
Choose size
Interval
Get your supplements at regular intervals with Autoship. At any time you can cancel the service or change the content or shipping interval.
See how to save with Autoship
- Description
- Data
- FAQ
- Reviews
Omega 3 Fish Oil supplements from Pharma Nord contain pure and natural fish oil in capsules made from fish gelatine. Omega 3 is important to normal immune system response and can also suppress the production of inflammatory substances. Fish oil contains omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, which contributes to normal functioning of the heart*. DHA contributes to the maintenance of normal vision** and brain function**.
Bio-Fish Oil is derived only from deep ocean fish and is carefully screened to ensure that it is free of possible pollutants. It is an economical fish oil preparation for a daily supplement.
* Min. 250 mg EPA/DHA a day
** Min. 250 mg DHA a day
Pure. Natural. Tasty! Fish oil as nature intended it.
What is Bio-Fish Oil?
Bio-Fish Oil contains omega 3 in its natural (triglyceride) form, that converts into free fatty acids in your digestive system before absorption. The unique aspect of this preparation is that the capsules are made of fish gelatine, making it 100% fish-derived. Our omega 3 fish oil supplements have a pleasant, natural lemon flavour added to each 500mg capsule. The fish used is caught in the cleaner waters of the South Pacific and Northern Atlantic.
- 90mg EPA per capsule
- 60mg DHA per capsule
The above ratios of EPA and DHA polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) represent the same levels found in nature. Bio-Fish Oil is not chemically or heat modified to claim higher levels.
More information on Omega 3 Fish Oil?
Our In-House team including our Senior Nutritionist has written articles on Omega 3 Fish Oil:
- Can Omega 3 help hair loss?
- Eating fish may lower risk of depression
Safety
| Nutritional Information | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Capsule contains: |
1 capsule | 5 capsules |
| Fish Oil | 500mg | 2500mg |
| EPA-content1) | 90mg | 450mg |
| DHA-content2) | 60mg | 300mg |
1) Eicosapentaenoic acid.
2) Docosahexaenoic acid.
Product Facts
Directions:
Adults: 5 capsules per day. Do not exceed recommended amount. Children from the age of 4: 2-3 capsules per day. Or as directed by a health professional. Content can be emptied out and taken by spoon.
Pregnant and lactating women and those on medication should seek professional advice prior to taking supplements.
Nutritional supplements should not be used as substitute for a varied diet and healthy lifestyle.
Customers who take anticoagulant medications should consult their doctor before taking omega 3 fish oil supplements.
Those on diabetic medication should seek professional advice prior to taking supplements.
Ingredients:
Fish oil
Capsule shell: Fish Gelatine
Humectant: Glycerol, Purified water
Aroma: Lemon flavour
Storage:
Room temperature and out of direct sunlight.
Keep out of reach of children.
Shelf Life:
Minimum 2 Years
* The beneficial effects is obtained with a daily intake of 250mg DHA.
** The beneficial effect is obtaining with a daily intake of 250mg of EPA and DHA.
|
About StatiQinon
StatiQinon are capsules containing a formula that effectively combines the action of red yeast rice with coenzyme Q10 and ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). ALA is an essential fatty acid that contributes to the maintenance of normal blood cholesterol concentrations (min. 450 mg of ALA a day).
How do traditional statins work in the body?
Statin medications remain an important medication for controlling cholesterol levels in those at risk of cardiovascular disease. Statins (also known as HMGCoA reductase inhibitors) have received criticism, however, for their potential side-effects, including muscular fatigue, weakness and pain 1.
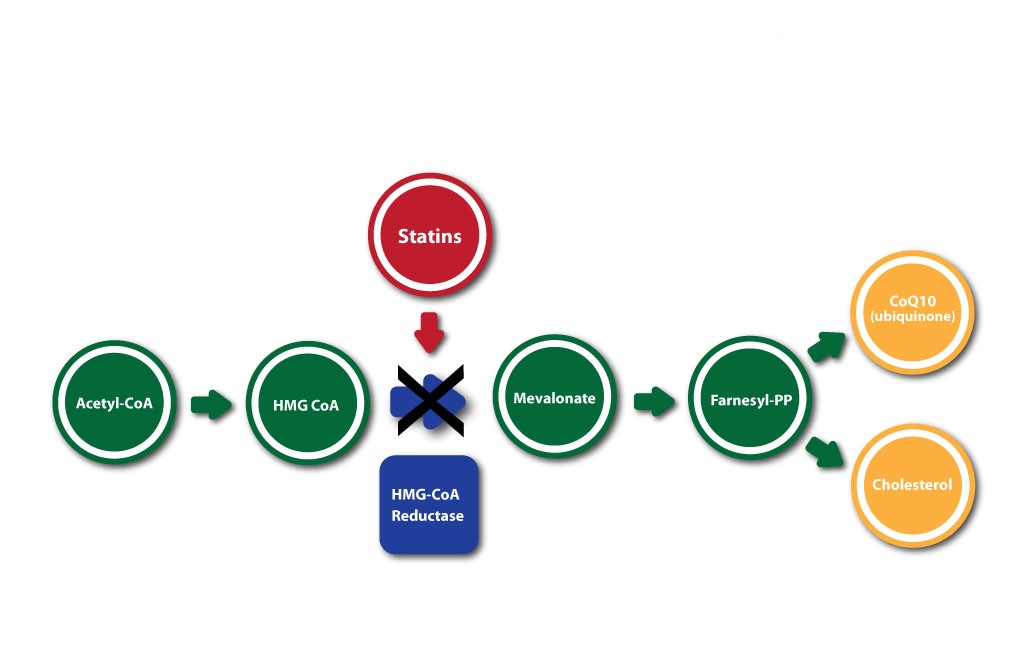
Statin medication lowers cholesterol by interrupting the mevalonate pathway, a chain of biochemical reactions the body uses to produce cholesterol. However, the actions of statins also reduce production of various other products made by the body, including CoEnzyme Q10. Evidence suggests that Q10 suppression brought about by statins may account for some of the side-effects of the treatment 2.
.png)
Graph: Atorvastatin decreases the coenzyme Q10 level in the blood of patients. 3
How does StatiQinon work?
StatiQinon combines the natural cholesterol-lowering potential of red yeast rice with protective coenzyme Q10 and ALA.
Red yeast rice - Natural statins
Statins are synthetically manufactured drugs intended for lowering cholesterol, but there are also naturally occurring statins. For instance, the oyster mushroom naturally contains lovastatin and natural statins are found in red yeast rice (RYR).
Produced by culturing rice with multiple yeast strains, RYR contains high levels of monacolin K- a substance that's structurally identical to the active ingredient in certain statins (such as lovastatin).
Red yeast rice extract works in a similar way to encourage healthy cholesterol levels. Randomized clinical trials have found natural statins to be both effective and well tolerated - also in most individuals who do not tolerate synthetic cholesterol-lowering drugs.
What is coenzyme Q10?
Coenzyme Q10 (Q10) is a vitamin-like substance found in the mitochondria in each of our cells, with one of Q10's main roles is to support energy production. Specifically, Q10 is mostly utilized in the 'electron transport chain', the final stage of respiration which converts our digested food into energy.
Busy organs such as the heart and skeletal muscles contain more mitochondria, undergo more respiration and have a great dependence on adequate Q10. Without adequate Q10, the heart and muscles may to work effectively.
Q10 supplementation is associated with a reduction in statin symptoms when taken alongside statins, and has been found to decrease muscle pain and weakness. 4,5
What is ALA?
ALA is short for ”alpha-linolenic acid”, a type of omega-3 fatty acid that is found in plants. ALA is an essential fatty acid meaning that it can't be produced by the body but must be obtained through the diet. Dietary sources for ALA include flaxseed, canola, soy, and walnuts. ALA is effective for maintaining normal cholesterol levels by decreasing circulating cholesterol.
References
1. Coenzyme Q10 and cardiovascular disease: an overview. British Journal of Cardiology. 2015;.
2. Langsjoen P, Langsjoen A. The clinical use of HMG CoA-reductase inhibitors and the associated depletion of coenzyme Q10. A review of animal and human publications. BioFactors.2003;18(1-4):101-111.
3. Atorvastatin decreases the coenzyme Q10 level in the blood of patients. Ref. Arch. Neurol. 2004 Jun;61(6): 889-92.
4. Caso G, Kelly P, McNurlan M, Lawson W. Effect of Coenzyme Q10 on Myopathic Symptoms in Patients Treated With Statins. The American Journal of Cardiology. 2007;99(10):1409-14
5. Fedacko J, Pella D, Rybar R, Fedackova P, Mechirova V. Abstract: 604 COENZYME Q10 AND SELENIUM SUPPLEMENTATION IN PATIENTS WITH STATIN-ASSOCIATED MYOPATHY. Atherosclerosis Supplements. 2009;10(2):e357.
6. Mortensen S, Rosenfeldt F, Kumar A, Dolliner P, Filipiak K, Pella D et al. The Effect of Coenzyme Q 10 on Morbidity and Mortality in Chronic HeartFailure. JACC: Heart Failure. 2014;2(6):641-649.
About Bio-Marine Plus
Fish oil describes oil from the body of fatty fish, a great source of Omega-3 fatty acids. These fatty acids are a group of essential, polyunsaturated fatty acids that are primarily found in oily fish like herring, salmon, and mackerel. The two most important omega-3 fatty acids are eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) which are important for a range of health benefits, including supporting heart health, brain health and vision.
Fish do not produce omega-3 fatty acids, but accumulate them by eating plankton, which in turn have higher omega-3 fatty acid levels the colder the sea water.
Why free fatty acids?
Fish oil must first be converted into free fatty acids before it can be absorbed by the human body. This conversion results in some loss of fatty acids. When you take fish oil as free fatty acids, you get 50% better absorption. This allows you to achieve the same effect with fewer capsules.
Why do we need to supplement?
Omega-3 is described scientifically as ‘essential’, meaning the human body is unable to produce it. We simply must obtain omega-3 fatty acids from the food we eat or the supplements we take.
Some of the healthiest diets in the world (including Japanese and Mediterranean) feature regular consumption of oily fish. Scientists first became aware of the link in the 1970s, when Danish clinicians discovered that Eskimos had exceptionally low rates of heart disease and arthritis, despite consuming a diet high in fats 1. It was then discovered that particular essential fatty acids (which we commonly refer to as omega-3) found within oily fish were to thank for these benefits.
Omega-3 levels are very low in land animals; oily fish (including salmon and mackerel) are good sources. In times when consuming these regularly becomes a challenge (due to cost or dislike of seafood), supplements serve as an ideal, practical solution.
How does it work in the body?
Fish oil is one of the best-researched nutritional supplements available with thousands of strong scientific studies supporting fish oils safety and benefits. EPA and DHA are beneficial in a wide range of systems around the body.
EPA & DHA are preferred by the body as they can be immediately used, whereas omega-3 from other sources (such as nuts and seeds) must be converted several times within the body, which is an ineffective process.
Fish oil works primarily through eicosanoids - fat-based signalling molecules which dictate how much inflammation the body will produce in response to physical stress, such as oxidation or inflammation. Fish oils encourage an anti-inflammatory response which, in turn, is associated with the reduction in risk of various diseases/ ailments.
Most omega-6 fatty acids (found in poultry, eggs, cereals and vegetable oils) are inflammatory by nature when consumed without adequate omega-3 to counter-balance them. Many experts agree that we should be at least balancing the amount of omega-6 we consume with omega-3 (a 1:1 ratio) to help reduce inflammation.
Benefits in Research
Brain health
250mg per day of DHA (as found in fish oil) contributes to the maintenance of a normal brain function. A wide array of clinical evidence supports the use of fish oil supplements in a range of mental wellbeing conditions, including depression 2.
A high proportion of brain tissue is made up of DHA and EPA, which are important both in forming the structure of brain cells and helping them communicate with each other. Low levels of DHA and EPA may affect concentration and mood in adults, and have been linked to learning difficulties and behavioural problems in growing children 3.
A meta-analysis from the Journal of the American College of Nutrition concluded that fish oil demonstrates a ‘significant antidepressant effect’ on a range of depression diagnoses including post-natal depression and major depressive disorder 4. In additional research, supplementation with omega 3 fatty acids has also been shown to reduce impaired cognitive function (such as memory issues) associated with ageing 5.
Homocysteine metabolism
Besides Omega 3 fatty acids, Bio-Marine Plus contains folic acid and vitamin B12. Both vitamins support the Omega 3 fatty acids in contributing to a normal homocysteine metabolism.
Homocysteine is a naturally occurring amino acid in the body. The metabolism of homocysteine is dependent on various vitamins including B12 and folic acid. Without adequate levels of these vitamins, the metabolism of homocysteine is impaired and levels of it begin to rise in the bloodstream.
Having elevated levels of homocysteine in the blood (hyperhomocysteinemia) is associated with fatty build-up in the arteries and stiffening of blood vessels, which may lead to blood clot formation, heart attack or stroke. Elevated homocysteine may also be associated with the development of Alzheimer's.
Other factors thought to raise levels of homocysteine include a poor diet, smoking, diabetes, arthritis and high consumption of diuretics such as coffee or alcohol.
Cardiovascular system
Omega-3 has shown the potential to inhibit cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), a protein the body produces and is associated with LDL cholesterol (the ‘bad cholesterol’), while suppressing it is associated with HDL cholesterol (the ‘good’ cholesterol). Omega 3 fatty acids in fish oil can help to maintain a healthy heart and blood vessels, healthy blood cholesterol and blood pressure levels 6,7.
Immunity and arthritis
Omega 3 fatty acids are also important in the normal functioning of the immune system, suppressing the production of inflammatory compounds in the body 8. This anti-inflammatory effect has shown benefits in research with sufferers of certain joint conditions.
A 2010 meta-analysis of studies concluded that fish oil significantly reduces symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, including joint stiffness and pain. The analysis also concluded that due to fish oil, the need for medication (such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) was decreased 9.
Attention issues in Children
Omega-3 supplementation has been shown to reduce symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) when compared to placebos. Studies also report that fish oil supplements were shown to be safe and tolerable in children 10.
Bio-Marine Plus
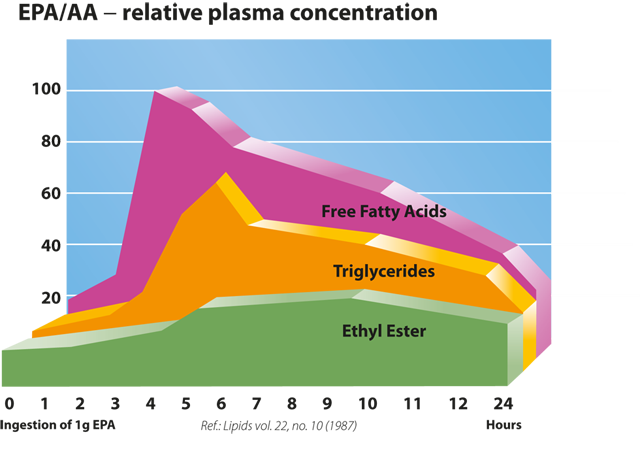
Fatty acid bioavailability
Omega 3 fish oils in the special free form present in Bio-Marine are assimilated and utilized by the body significantly better than both triglycerides and ethyl esters, used in other fish oil products 11.
High Purity
The fish oil in Bio-Marine Plus demonstrates a very high level of purity as the oil has undergone a three-step refining process, where the oil is thoroughly cleaned. One of the world’s leading technologies is used for screening and removing unwanted particles like pesticides, heavy metals, furans (highly toxic waste particles from industrial burning) etc. This means that the content of several of these potentially harmful compounds may be far below the official threshold levels approved for fish and fish oil products.
The fact that the oil in Bio-Marine Plus is very clean was confirmed in a survey of pollutants in a number of fish oil products made in 2018 12 at the request of the independent Danish consumer organization TÆNK. The study found the following extremely low pollution values:
Mercury (Hg): at least 95% below the EU permitted content of mercury.
Dioxin: 98% below the EU allowed limit on dioxin and dioxin-like PCBs.
Equivalent of 4-5 oily fish per week
A Finnish study that was published in a scientific journal 13 demonstrated that people who consumed Bio-Marine daily had the same health benefit as those who ate a fish meal four to five times per week.
Protected
Bio-Marine Plus is encapsulated in an oxygen-free environment and has an extremely low peroxide count due to the fact that the oil is effectively protected against oxidation. When oils are oxidized, they lose their nutritional benefits and become unpleasant and ‘rancid’.
References
1. Bang H, Dyerberg J, Nielsen A. PLASMA LIPID AND LIPOPROTEIN PATTERN IN GREENLANDIC WEST-COAST ESKIMOS. The Lancet. 1971;297(7710):1143-1146.
2. Sublette M, Ellis S, Geant A, Mann J. Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) in Clinical Trials in Depression. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2011;72(12):1577-1584.
3. Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and the brain: a review of the independent and shared effects of EPA, DPA and DHA
4. Martins J. EPA but Not DHA Appears To Be Responsible for the Efficacy of Omega-3 Long Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation in Depression: Evidence from a Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of the American College of Nutrition. 2009;28(5):525-542.
5.Schaefer E, Bongard V, Beiser A, Lamon-Fava S, Robins S, Au R et al. Plasma Phosphatidylcholine Docosahexaenoic Acid Content and Risk of Dementia and Alzheimer Disease. Archives of Neurology. 2006;63(11):1545.
6. Simão A, Lozovoy M, Bahls L, Morimoto H, Simão T, Matsuo T et al. Blood pressure decrease with ingestion of a soya product (kinako) or fish oil in women with the metabolic syndrome: role of adiponectin and nitric oxide. British Journal of Nutrition. 2012;108(8):1435-1442.
7. Ramel A, Martinez J, Kiely M, Bandarra N, Thorsdottir I. Moderate consumption of fatty fish reduces diastolic blood pressure in overweight and obese European young adults during energy restriction. Nutrition. 2010;26(2):168-174.
8. Maroon J, Bost J. ω-3 Fatty acids (fish oil) as an anti-inflammatory: an alternative to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for discogenic pain. Surgical Neurology. 2006;65(4):326-331.
9. James M, Proudman S, Cleland L. Fish oil and rheumatoid arthritis: past, present and future. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society. 2010;69(3):316-323.
10. Bélanger S, Vanasse M, Spahis S, Sylvestre M, Lippé S, l'Heureux F et al. Omega-3 fatty acid treatment of children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Paediatrics & Child Health. 2009;14(2):89-98.
11.Lipids. 1987;22(10).
12.Forbrugerrådet Tænk februar 2019 [Internet]. Forbrugerrådet Tænk. 2019 [cited 14 May 2019]. Available from: https://taenk.dk/om-os/magasinet-forbrugerraadet-taenk/2019/februar-198
13. J. Agren et al. 1996; Eur. Journal of Clinical Nutrition 50;765-71.
About fish oil
Fish oil describes oil from the body of fatty fish, a great source of Omega-3 fatty acids. These fatty acids are a group of essential, polyunsaturated fatty acids that are primarily found in oily fish like herring, salmon, and mackerel. The two most important omega-3 fatty acids are eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) which are important for a range of healthy benefits, including supporting heart health, brain health and vision.
Fish do not produce omega-3 fatty acids, but accumulate them by eating plankton, which in turn have higher omega-3 fatty acid levels the colder the sea water.
Why do we need to supplement?
Omega-3 is described scientifically as ‘essential’, meaning the human body is unable to produce them. We simply must obtain omega-3 fatty acids from the food we eat or the supplements we take.
Some of the healthiest diets in the world (including Japanese and Mediterranean) feature regular consumption of oily fish. Scientists first became aware of the link in the 1970s, when Danish clinicians discovered that Eskimos had exceptionally low rates of heart disease and arthritis, despite consuming a diet high in fats 1. It was then discovered that particular essential fatty acids (which we commonly refer to as omega-3) found within oily fish were to thank for these benefits.
Omega-3 levels are very low in land animals; oily fish (including salmon and mackerel) are good sources. In times when consuming these regularly becomes a challenge (due to cost or dislike of seafood), supplements serve as an ideal, practical solution.
How does it work in the body?
Fish oil is one of the best-researched nutritional supplements available with thousands of strong scientific studies supporting fish oils safety and benefits. EPA and DHA are beneficial in a wide range of systems around the body.
EPA & DHA are preferred by the body as they can be immediately used, whereas omega-3 from other sources (such as nuts and seeds) must be converted several times within the body, which is an ineffective process.
Fish oil works primarily through eicosanoids - fat-based signalling molecules which dictate how much inflammation the body will produce in response to physical stress, such as oxidation or inflammation. Fish oils encourage an anti-inflammatory response which in turn, is associated with the reduction in risk of various diseases/ ailments.
Most omega-6 fatty acids (found in poultry, eggs, cereals and vegetable oils) are inflammatory by nature when consumed without adequate omega-3 to counter-balance them. Many experts agree that we should be at least balancing the amount of omega-6 we consume with omega-3 (a 1:1 ratio) to help reduce inflammation.
Benefits in Research
Cardiovascular system
Omega-3 has shown the potential to inhibit cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), a protein the body produces and is associated with LDL cholesterol (the ‘bad cholesterol’), while suppressing it is associated with HDL cholesterol (the ‘good’ cholesterol). Omega 3 fatty acids in fish oil can help to maintain a healthy heart and blood vessels, healthy blood cholesterol and blood pressure levels 2,3.
Immunity and arthritis
Omega 3 fatty acids are also important in the normal functioning of the immune system, suppressing the production of inflammatory compounds in the body 4. This anti-inflammatory effect has shown benefits in research with sufferers of certain joint conditions.
A 2010 meta-analysis of studies concluded that fish oil significantly reduce symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, including joint stiffness and pain. The analysis also concluded that due to fish oil, the need for medication (such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) was decreased 5.
Brain health
250mg per day of DHA (as found in fish oil) contributes to the maintenance of a normal brain function. A wide array of clinical evidence supports use of fish oil supplements in a range of mental wellbeing conditions.
A high proportion of brain tissue is made up of DHA and EPA, which are important both in forming the structure of brain cells and helping them communicate with each other. Low levels of DHA and EPA may affect concentration and mood in adults, and have been linked to learning difficulties and behavioural problems in growing children 6.
A meta-analysis from the Journal of the American College of Nutrition concluded that fish oil demonstrates a ‘significant antidepressant effect’ on a range of depression diagnoses including post-natal depression and major depressive disorder 7. In additional research, supplementation with omega 3 fatty acids has also been shown to reduce impaired cognitive function (such as memory issues) associated with ageing 8.
Attention issues in Children
Omega-3 supplementation has been shown to reduce symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) when compared to placebos. Studies also report that fish oil supplements were shown to be safe and tolerable in children 9.
Bio-Fish Oil & BIOmega-3 Kids
High quality fish oil should be derived only from deep ocean fish (not farmed fish), and carefully screened to ensure that it is free from possible pollutants such as heavy metals. Oil extracted from the body of the fish (rather than the liver) is free of vitamin A which would otherwise be toxic at high levels.
For many health benefits associated with fish oil supplementation, it’s suggested that EPA should make up at least 60% of the supplements content, with the remainder as DHA.
Bio-Fish Oil from Pharma Nord contains pure fish oil with the optimal balance of omega-3 fatty acids and is made to pharmaceutical standards. It also comes with a pleasant natural lemon flavour to avoid that fishy aftertaste common to many fish oil supplements.
References
1. Bang H, Dyerberg J, Nielsen A. PLASMA LIPID AND LIPOPROTEIN PATTERN IN GREENLANDIC WEST-COAST ESKIMOS. The Lancet. 1971;297(7710):1143-1146.
2. Simão A, Lozovoy M, Bahls L, Morimoto H, Simão T, Matsuo T et al. Blood pressure decrease with ingestion of a soya product (kinako) or fish oil in women with the metabolic syndrome: role of adiponectin and nitric oxide. British Journal of Nutrition. 2012;108(8):1435-1442.
3. Ramel A, Martinez J, Kiely M, Bandarra N, Thorsdottir I. Moderate consumption of fatty fish reduces diastolic blood pressure in overweight and obese European young adults during energy restriction. Nutrition. 2010;26(2):168-174.
4. Maroon J, Bost J. ω-3 Fatty acids (fish oil) as an anti-inflammatory: an alternative to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for discogenic pain. Surgical Neurology. 2006;65(4):326-331.
5. James M, Proudman S, Cleland L. Fish oil and rheumatoid arthritis: past, present and future. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society. 2010;69(3):316-323.
6. Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and the brain: a review of the independent and shared effects of EPA, DPA and DHA
7. Martins J. EPA but Not DHA Appears To Be Responsible for the Efficacy of Omega-3 Long Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation in Depression: Evidence from a Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of the American College of Nutrition. 2009;28(5):525-542.
8. Schaefer E, Bongard V, Beiser A, Lamon-Fava S, Robins S, Au R et al. Plasma Phosphatidylcholine Docosahexaenoic Acid Content and Risk of Dementia and Alzheimer Disease. Archives of Neurology. 2006;63(11):1545.
9. Bélanger S, Vanasse M, Spahis S, Sylvestre M, Lippé S, l'Heureux F et al. Omega-3 fatty acid treatment of children withAbout the nutrient
Carnitine is a non-essential, water-soluble amino acid. One of the roles of carnitine in the body is its contribution to the mitochondrial oxidation of long-chain fatty acids obtained from the diet. Most of the body's carnitine supply is stored in muscle tissue, including the heart muscle. Normal seminal fluid also contains carnitine.
Why do we need to supplement?
Carnitine is non-essential, meaning the body can produce some by itself, via the amino acid lysine. Our production of this amino acid (and therefore our total levels) drop with increasing age.
Carnitine is found in some dietary sources such as red meat and limited quantities in plant protein. It is for this reason that vegetarians (and vegans) often have much lower levels of this amino acid.
How does it work in the body?
L-carnitine’s main mode of action is supporting the transfer of fat (derived from our diet) into the mitochondria of the cell, where they are metabolised.
The mitochondria is a part of the cell often referred to as the ‘powerhouse’. Mitochondria (with the help of various nutrients including coenzyme Q10 and l-carnitine) are able to convert the broken-down elements of our food, such as glucose, into energy. L-carnitine operates by being part of the substances carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 & 2, enzymes that act as a shuttle for ‘fatty acids’, a simple unit of fat which all dietary fats convert to after digestion. L-carnitine allows these fatty acids to be delivered into the mitochondria (after being converted to Acyl Co-A), where they can be metabolised via the process of B-oxidation, converting the fat into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) - the body’s unit of energy.
Benefits in Research
Reduction in body fat and fatigue
Studies have shown promise in L-carnitine’s ability to support the reduction of body fat. In one randomized control-trial comparing an L-carnitine supplementation group of patients with a group taking placebos, the treatment group experienced a significant reduction in body fat compared to placebo (-3.1kg vs -0.5kg) 1 .
The main mechanism proposed for this is that L-carnitine supports the use of fat as an energy source, including stored body fat.
Athletic performance
Dietary fats are more energy dense than carbohydrates or proteins, with 9 kcals per gram versus 4 kcals per gram. As L-carnitine grants greater access to this rich source of energy, it’s theorized that L-carnitine would support athletic performance. Various studies have shown that supplementation with L-carnitine can offer a range of benefits which would support athletic activity, including improved stamina, better oxygenation of muscles and decreased recovery times between exertion 2,3.
Bio-Carnitine utilizes the L-tartrate form of carnitine, considered to be the superior carnitine form for athletic performance.
Sperm Quality
In various trials, carnitine supplementation has been shown to be an effective method of improving sperm quality, especially morphology (or shape). The proposed reason for this benefit is that carnitine effectively shuttles fatty acids into the mitochondria of the sperm cells, providing them with cellular energy, but is also shown to protect the cells and DNA from oxidative stress 4.
Cognition
Some research shows that L-carnitine supplementation can support cognition and general mental processes, including memory and learning 5.
Bio-Carnitine
The carnitine in Bio-Carnitine is produced by means of a unique manufacturing technique based on fermentation. This method that carries the 'Carnipure' quality stamp makes it possible to produce L-carnitine exactly like it is done in nature. The result is pure, nature-identical L-carnitine L-Tartrate without residues of D-carnitine.
What is Carnipure?
Carnipure® is L-carnitine in an exceptionally pure form, manufactured to the highest standards of production quality and traceability of raw materials. This means that all batches of Carnipure can be traced directly back to their origin from the unprocessed raw materials to the finished extract. It is a guarantee of a high quality product with standardized efficiency, purity and quality in each capsule.
References
1. Pistone G, Marino A, Leotta C, Dell???Arte S, Finocchiaro G, Malaguarnera M. Levocarnitine Administration in Elderly Subjects with Rapid Muscle Fatigue. Drugs & Aging. 2003;20(10):761-767.
2. KRAEMER W, VOLEK J, FRENCH D, RUBIN M, SHARMAN M, GOMEZ A et al. The Effects of L-Carnitine L-Tartrate Supplementation on Hormonal Responses to Resistance Exercise and Recovery. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research. 2003;17(3):455-462.
3. Spiering B, Kraemer W, Hatfield D, Vingren J, Fragala M, Ho J et al. Effects of L-Carnitine L-Tartrate Supplementation on Muscle Oxygenation Responses to Resistance Exercise. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research. 2008;22(4):1130-1135.
4. Lenzi A, Lombardo F, Sgrò P, Salacone P, Caponecchia L, Dondero F et al. Use of carnitine therapy in selected cases of male factor infertility: a double-blind crossover trial. Fertility and Sterility. 2003;79(2):292-300.
5. Malaguarnera M, Gargante M, Cristaldi E, Colonna V, Messano M, Koverech A et al. Acetyl l-carnitine (ALC) treatment in elderly patients with fatigue. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics. 2008;46(2):181-190.
See related categories
Omega 3 Fish Oil Supplements In Research

Related articles

News
Taking vitamin D during pregnancy is good for the ...24/01/2025
New study shows that a daily vitamin D supplement during pregnancy can support the child’s bone heal...
.jpg?w=285&quality=100)
News
StatiQinon - For normal cholesterol levels07/09/2020
StatiQinon are capsules containing a formula that effectively combines the action of red yeast rice ...






.jpg?w=285&quality=100)
.jpg?w=285&quality=100)
.jpg?w=285&quality=100)




