What are Vitamin B12 Supplements?
- High dose, tasty lozenges and chewable tablets.
- Methylcobalamin - 'Active' form of B12.
- Highly bioavailable.
- Suitable for vegetarians and vegans.
- Manufactured under Danish pharmaceutical control.
Bio-Vitamin B12
Bio-Vitamin B12
£13.96You save £2.09
Interval
Get your supplements at regular intervals with Autoship. At any time you can cancel the service or change the content or shipping interval.
See how to save with Autoship
- Description
- Data
- FAQ
- Reviews
Bio-Vitamin B12 supplements from Pharma Nord delivers vitamin B12 in an advanced, effective and bioavailable form.
Vitamin B12 is an important nutrient that contributes to energy-yielding metabolism, the reduction of tiredness and fatigue and the nervous and immune systems. B12 is also important to support red blood cell formation and psychological function.
Why Pharma Nord Vitamin B12 Supplements?
A Lack of B12
Not having enough vitamin B12 in the diet may be associated with various symptoms including tiredness and fatigue, and may even lead to a condition called pernicious anemia.
B12 is a vitamin found primarily from meats and other animal-based foods. Vegetarians and vegans therefore, may be low in this essential vitamin and may require an effective supplement to ensure healthy levels.
Why is Vitamin B12 Absorption Important?
For the human body, digesting and absorbing vitamin B12 requires a special protein known as ‘intrinsic factor’ which is produced in the stomach. Some people don’t produce enough of this protein and therefore can’t effectively absorb B12 from their food. This may also be an issue for those of us who take certain medications for high stomach acid, or those that have digestive issues involving low stomach acid.
When we dissolve the Bio-Vitamin B12 lozenge in the mouth, the vitamin is absorbed directly from the mucous membranes of the mouth, bypassing the rest of the digestive system.
What Does 'Active B12' Mean?
Bio-Vitamin B12 uses an advanced form of vitamin B12 called ‘methylcobalamin’. Compared to the more common synthetic ‘cyanocobalamin’ types, methylcobalamin is found in nature.
Methylcobalamin is the only form of B12 directly engaged in the metabolism of homocysteine, converting it to methionine and then S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), which is helps support production of hormones and neurotransmitters (including those that affect mood).
| One Tablet Contains: | %NRV* | |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin B12 | 600mcg | 24,000% |
* NRV: Nutrient Reference Value.
Product Facts
Directions:
Adults: 1-2 tablets daily or as recommended by a physician. Tablets can be chewed.
Do not exceed recommended amount, excessive consumption may product laxative effects.
Suitable for vegetarians and vegans.
Pregnant and lactating women and those on medication should seek professional advice prior to taking supplements.
Nutritional supplements should not be used as a substitute for a varied diet and a healthy lifestyle.
Ingredients:
Sweetener: Xylitol
Food stuff: Maltodextrin
Flavour enhancer: Glycine
Anti-Caking Agent: Polyvinylpyrrolidone
Anti-Caking Agent: Magnesium salts of fatty acid
Flavouring: Peppermint powder
Vitamin B12: Methylcobalamin
Storage:
Room temperature out of direct sunlight. Keep out of reach of children.
Shelf Life:
Minimum 2 years.
About Vitamin K2
Vitamin K2 is a fat-soluble vitamin which is important for the maintenance of normal bone health, cardiovascular health and normal blood clotting. Being active in the body for longer than vitamin K1; vitamin K2 is able to reach more tissue and activate proteins that have a role in keeping calcium mobile.
Why do we need to supplement?
Vitamin K2 is challenging to obtain from the diet. To obtain 75μg per day, a person would need to consume 7kg of beef, 8.5 litres of milk or 14 eggs. A rich source of K2 is found within the Japanese dish 'natto' – a fermented soybean dish not commonly consumed around the world.
How does it work in the body?
K2 is beneficial to anyone who wants to take care of their bone health and circulatory health as it may help maintain bone strength and density while protecting blood vessels from hardening. It does this via the activation of 'K-dependent' proteins osteocalcin (OC) and matrix Gla-protein (MGP).
MGP transports calcium away from where it can cause harmful hardening of soft tissue (i.e. calcification) and towards the bones where it contributes to their strength and structure.
Benefits in Research
Bone Health
The skeleton is fully replaced approximately every seven years thanks to specialist bone cells. Older bone is broken down by osteoclast cells while new bone is built via osteoblast cells. Osteoblasts slow with age and when osteoclast activity is in excess, it contributes to bones becoming porous and fragile. When severe enough, this is diagnosed as osteoporosis and carries with it an increased risk of fractures.
Having adequate vitamin K2 can assist, however, via the activation of the protein osteocalcin. K2 activates osteocalcin via an enzyme co-factor, enabling calcium to be incorporated into the bone matrix, building new bone and contributing to bone density. Osteoclast cell activity may also be inhibited by adequate K, further slowing bone breakdown 1.
Cardiovascular health
Vitamin K has been shown in studies to assist in the maintenance of circulatory health if taken daily. Vitamin K2 acts as a cofactor for activation of Matrix Gla Protein (MGP) which is located in the cartilage and smooth muscle cells of the vascular system. When activated, MGP can inhibit soft tissue calcification which could otherwise build up leading to elevated cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk.
A 2004 population-based study (known as the Rotterdam Study) explored the relationship between vitamin K intake and CVD with 4807 subjects.
The group with adequate vitamin K intakes experienced:
• Reduced CVD and Death from CVD
• Reduced severe calcification of the blood vessels
• Reduced all-cause mortality
.png)
The lead researcher discussed that this effect may be due to reduction in arterial calcification and suggests that elevated intakes of vitamin K2 contribute to heart disease prevention 2.
K-Pearls
K-Pearls contain vitamin K2 in the menaquinone-7 (MK-7) form which has shown to be the most beneficial form of vitamin K2 according to recent research. Due to staying in the body longer than the other form of vitamin K2, MK-4, MK-7 is able to activate proteins Matrix Gla and osteocalcin better which are associated with the vitamin’s health benefits.
Studies have also shown that MK-7 demonstrates superior effects on normal blood coagulation compared to MK-4 3 and provides a more active grade of osteocalcin than Vitamin K14.
100% Active form
Vitamin K2 MK-7 can be sourced from either Natto (soy processed via fermentation) or produced via a patented organic process using flower material, the latter being a newer scientific development.
K2 MK-7 produced via the organic process demonstrates a 100% trans MK-7 profile, with the trans form being the only biologically active form. In essence, MK-7 produced this way is 100% trans and biologically active whereas MK-7 produced via fermentation processes is partially active, being a mix of both active trans and inactive cis forms.
Bioavailable
K2 is 'lipid soluble', so it is best absorbed by the body in the presence of fats. Bio-Vitamin K2 comes in small, easy to swallow oil capsules to help ensure digestive absorption.
Allergen-free
The organic process also produces K2 MK-7 which is free of common allergens, great news for individuals adverse to soy present in the fermented varieties.
References
1. Akbari S, Rasouli-Ghahroudi A. Vitamin K and Bone Metabolism: A Review of the Latest Evidence in Preclinical Studies. BioMed Research International. 2018;2018:1-8.
2. M. Geleijnse J, Vermeer C. Dietary Intake of Menaquinone Is Associated with a Reduced Risk of Coronary Heart Disease: TheRotterdam Study. The Journal of Nutrition. 2014;134:3100 –3105.
3. Groenen-Van Dooren M, Ronden J, Soute B, Vermeer C.Bioavailability of phylloquinone and menaquinones after oral and
colorectal administration in vitamin K-deficient rats. BiochemicalPharmacology. 1995;50(6):797-801.
4. Schurgers L, Teunissen K, Hamulyak K, Knapen M, Vik H, VermeerC. Vitamin K-containing dietary supplements: comparison of
synthetic vitamin K1 and natto-derived menaquinone-7. Blood.2007;109(8):3279-3283.
B-Daddy contains two patented ingredients: The selenium yeast SelenoPrecise® and Bio-Quinone Q10.
The quality of both active ingredients is documented in an array of scientific studies. Selenium protects the body's cells against oxidative damage, while coenzyme Q10 contributes to the body's energy metabolism inside each cell. In this way the two nutrients in B-Daddy support the production of normal, healthy sperm cells.
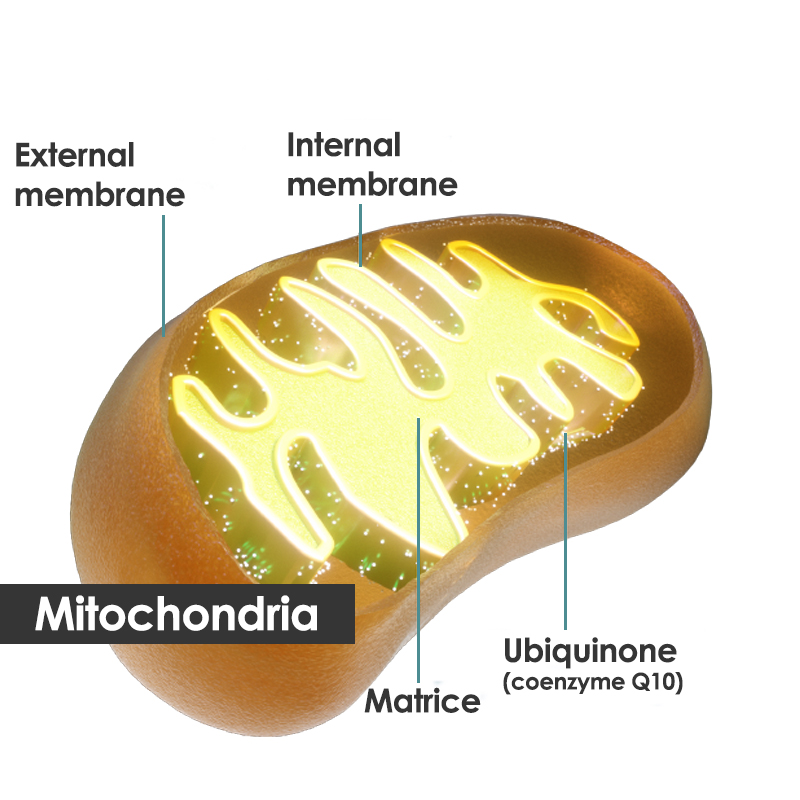
How does it work in the body?
Coenzyme Q10 (Q10) helps the cellular powerhouses (mitochondria) produce energy from the food we consume. This process also takes place inside sperm cells. The source of Q10 used in Pharma Nord's B-Daddy is exactly the same as the Q10 that is synthesized by the human body and has superior bioavailability. Bio-Quinone Q10 is the official reference preparation of the ICQA (the International Coenzyme Q10 Association) and is preferred by doctors and scientists worldwide.
Selenium is an essential trace element that supports a variety of different selenium-dependent proteins (selenoproteins) that are vital for human health and well-being. The selenium used in B-Daddy is the Danish, patented selenium yeast SelenoPrecise® that contains 30 different organically bound selenium compounds. This particular selenium yeast is able to document that 88.7% of its selenium content is absorbed in the human body. In addition to selenium's protective effect on cells, the nutrient is also known to support:
- A normal and well-functioning immune defense
- Normal growth
- The production of normal, healthy sperm cells
Male fertility
An average male ejaculation delivers between 60 and 450 million microscopic sperm cells. The sperm fluid contains different sugars that serve as nutrition for the sperm cells and help them stay viable for about 2-3 days. Sperm cells are matured in the testicles, a process that takes about 74 days to complete. However, as there are several million sperm-producing glands in the testicles, each testicle can produce four million sperm cells an hour.
Anatomically speaking, a sperm cell consists of a head, a mid-piece, and a long, moveable tail. The head contains the cell nucleus with the genetic material inside. The mid-section is saturated with mitochondria. Inside every mitochondria Q10 is found. The mitochondria supply the energy needed to fuel the rapid tail movements that propel the sperm cell on its long journey to reach the egg cell.
The sperm cells are some of the body’s most energy-consuming cells. They need the energy to swim the relatively long way from the woman’s vagina through her uterus to the fallopian tube where the egg is fertilized. It is like a race where very few sperm cells are able to complete the 15-25 cm distance to the egg.
The more healthy sperm cells a man is able to produce, and the faster they are able to swim, the greater the chances of successful conception. This is where B-Daddy comes in as a useful remedy that can ensure the production of normal, healthy sperm cells.
Benefits in Research
Selenium in male fertility
Selenium contributes to normal spermatogenesis; the process in which sperm is made. Various trials demonstrate that adequate selenium supports male fertility.
A 2009 study1 involved 116 infertile men receiving 200 μg of selenium daily versus a group taking a placebo. It was found that supplementation with selenium had significantly increased total sperm count and motility compared to placebo. The
researchers noted there was no adverse effects of the selenium supplementation.
Q10 in male fertility
In one trial, researchers enrolled 212 infertile men with various sperm abnormalities. Half of the patients were randomly assigned to receive 300 milligrams of Coenzyme Q10 daily, and half took matching placebos for 26 weeks. The researchers then continued to follow the patients’ progress for a 30-week treatment-free phase.
The Coenzyme Q10 treatment resulted in significant improvement in sperm count, sperm motility and the percentage of normally formed sperm. 2
In another trial, researchers assigned 55 patients with abnormal sperm parameters to a treatment group taking 200 milligrams of Coenzyme Q10 or placebo daily for three months,followed by three months of follow-up. The results showed that Coenzyme Q10 significantly increased CoQ10 levels in seminal plasma and sperm cells. The CoQ10 supplementation was also significantly associated with increased sperm cell total motility and forward motility. The researchers noted the greatest response in the patients who had the lower baseline sperm motility levels and the lower baseline levels of CoQ10.
After three months of wash-out following the end of the six-month treatment period, the researchers found that the sperm cell total motility and forward motility were greatly reduced compared with the levels at the end of the six-month treatment period. 3
References
1.Safarinejad, M. R., & Safarinejad, S. (2009). Efficacy of selenium and/or N-acetyl-cysteine for improving semen parameters in infertile men: a double-blind, placebo controlled, randomized study. The Journal of Urology,181(2), 741-751.
2.Safarinejad, M. R. (2009). Efficacy of Coenzyme Q10 on semen parameters, sperm function and reproductive hormones in infertile men. The Journal Of Urology, 182(1), 237–248.
3. Balercia, G., Buldreghini, E., Vignini, A., Tiano, L., Paggi, F., Amoroso, S., & Littarru, G. (2009). Coenzyme Q10 treatment in infertile men with idiopathic asthenozoospermia: a placebo-controlled, double-blind randomized trial. Fertility And Sterility, 91(5), 1785–1792.
|
|
.png)

By Frankie Brogan
Senior Nutritionist
Tired all the time? You’re not alone.
Tiredness is one of the most common health complaints we have in the UK.1 Tiredness can be a tricky problem to overcome, however, as there are many potential causes. Medical conditions, the stresses of daily life and poor sleep quality can all be culprits. Low levels of certain nutrients can also lead to tiredness, so making sure we get all the right nutrients in our diet is essential.
Here, we’ll talk about some of the most common nutritional shortfalls to consider when trying to safeguard your energy levels.
1) Iron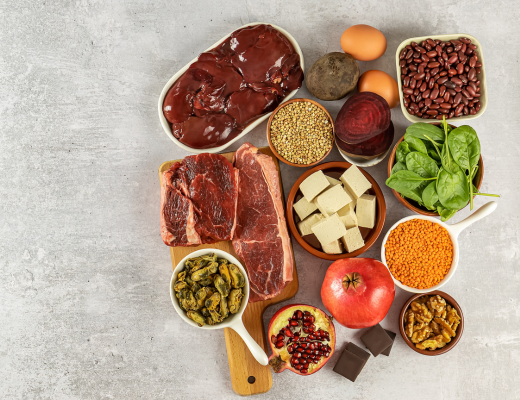 
This mineral is important for the proper production of red blood cells which carry oxygen throughout the body. This oxygen is needed for ‘cellular respiration’; a process in which our cells convert our digested food into energy. Low iron can lead to ‘iron deficiency anaemia’, associated with tiredness and fatigue.
Iron can be found in both animal foods such as red meat, poultry, and plant foods, such as green leafy vegetables, legumes, and sesame seeds.
It’s worth noting that non-animal-based iron (also known as ‘non-heme’) does not absorb as well as animal-based iron. This absorption can be improved, however, by supplementing your dietary iron intake with vitamin C.2
2) B12 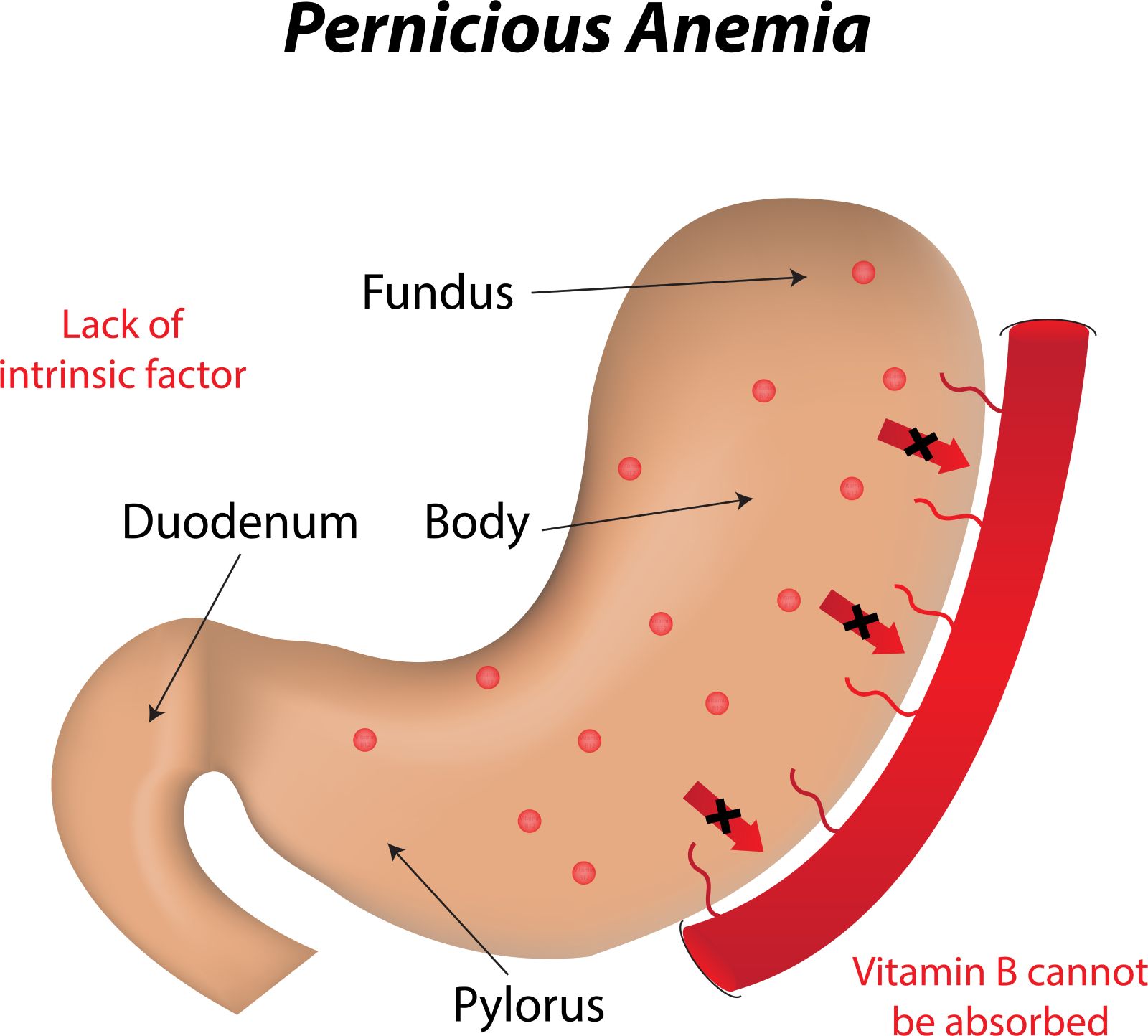
As with Iron, vitamin B12 is essential for the production of oxygen-delivering red blood cells and therefore supports energy-yielding metabolism.
B12 is found primarily in animal foods such as meats and dairy products, so vegetarians and vegans may be at a higher risk of missing out without consuming B12 fortified plant-foods or supplements.
If considering supplementing with B12, note that some people have difficulty absorbing this vitamin through the gut as they lack something known as ‘intrinsic factor’ which is used to transport B12 through the digestive tract. This may include people with the autoimmune condition ‘pernicious anaemia’.
For this reason, B12 which is formulated to absorb in the mouth (such as a pastille) rather than being swallowed whole, can be especially effective.
3) Other B vitamins
As well as B12, other B vitamins are very important for optimum energy production. Vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, and B3 all contribute to energy-providing metabolism.
Vitamin B3 (niacin) is especially important to consider as the body uses it as a precursor to produce the compound, NADH. NADH works alongside the vitamin-like compound coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) in the mitochondria, the part of the cell responsible for energy-providing metabolism.3
4) Coenzyme Q10
Speaking of CoQ10, this is another compound used by the mitochondria, which are often known as the ‘batteries’ or the ‘powerhouses’ of the cells. Thanks to the help of compounds such as CoQ10, these mitochondria convert the food we eat into the molecule ‘ATP’ (adenosine triphosphate). This ATP molecule can then be used by the body to release energy.
We naturally produce CoQ10 in the body, but unfortunately, research has shown that this production can decline for various reasons, including the natural ageing process. This combined with a lack of substantial dietary sources has resulted in CoQ10 supplementation becoming a popular consideration.4
5) Magnesium
Magnesium contributes to the reduction of tiredness and fatigue, but how?
This mineral is the real workhorse of nutrients being involved in over 600 different enzymatic reactions in the body, including energy-providing metabolism. As mentioned earlier, when we eventually metabolise our food, the mitochondria produce the molecule ATP which is used for energy. However, before this ATP can actually be used by the body, it must first combine with magnesium.5
Dietary sources of magnesium include spinach, nuts, and whole grains. Dietary intakes of magnesium in the UK are low, however, resulting in an increased interest in magnesium supplements.6
Learn more about our supplements >
References:
1. Stadje R, Dornieden K, Baum E, et al. The differential diagnosis of tiredness: a systematic review. BMC Fam Pract. 2016;17(1):147. Published 2016 Oct 20. doi:10.1186/s12875-016-0545-5
2. Cook JD, Monsen ER. Vitamin C, the common cold, and iron absorption. Am J Clin Nutr. 1977;30(2):235-241. doi:10.1093/ajcn/30.2.235
3. Pirinen E, Auranen M, Khan NA, et al. Niacin Cures Systemic NAD+ Deficiency and Improves Muscle Performance in Adult-Onset Mitochondrial Myopathy [published correction appears in Cell Metab. 2020 Jul 7;32(1):144]. Cell Metab. 2020;31(6):1078-1090.e5. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.008
4. Aaseth J, Alexander J, Alehagen U. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation - In ageing and disease. Mech Ageing Dev. 2021;197:111521. doi:10.1016/j.mad.2021.111521
5. Yamanaka R, Tabata S, Shindo Y, et al. Mitochondrial Mg(2+) homeostasis decides cellular energy metabolism and vulnerability to stress. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30027. Published 2016 Jul 26. doi:10.1038/srep30027
6. Derbyshire E. Micronutrient Intakes of British Adults Across Mid-Life: A Secondary Analysis of the UK National Diet and Nutrition Survey. Front Nutr. 2018;5:55. Published 2018 Jul 19. doi:10.3389/fnut.2018.00055
See related categories
Bio-Vitamin B12 in research

Related articles

News
Selenium and Q10 are important for seniors12/07/2024
Scandinavian researchers have published a study that demonstrates how a combination of selenium and ...
.jpg?w=285&quality=100)
News
The majority of Europeans get far too little of th...01/09/2023
Nearly half of the Irish population fails to get enough of the essential nutrient selenium, even tho...
%20(1).png?w=285&quality=100)
News
How to tackle tiredness - 5 key nutrients21/06/2023
Tired all the time? You’re not alone. Tiredness is one of the most common health complaints we have ...










.jpg?w=285&quality=100)
.jpg?w=285&quality=100)




